What is Sustainable Design in Construction
Sustainable design and construction refer to practices that aim to minimize the environmental impact of buildings and infrastructure throughout their entire lifecycle. This approach integrates environmental, social, and economic considerations to create structures that are efficient, resource-conscious, and socially responsible. The goal is to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
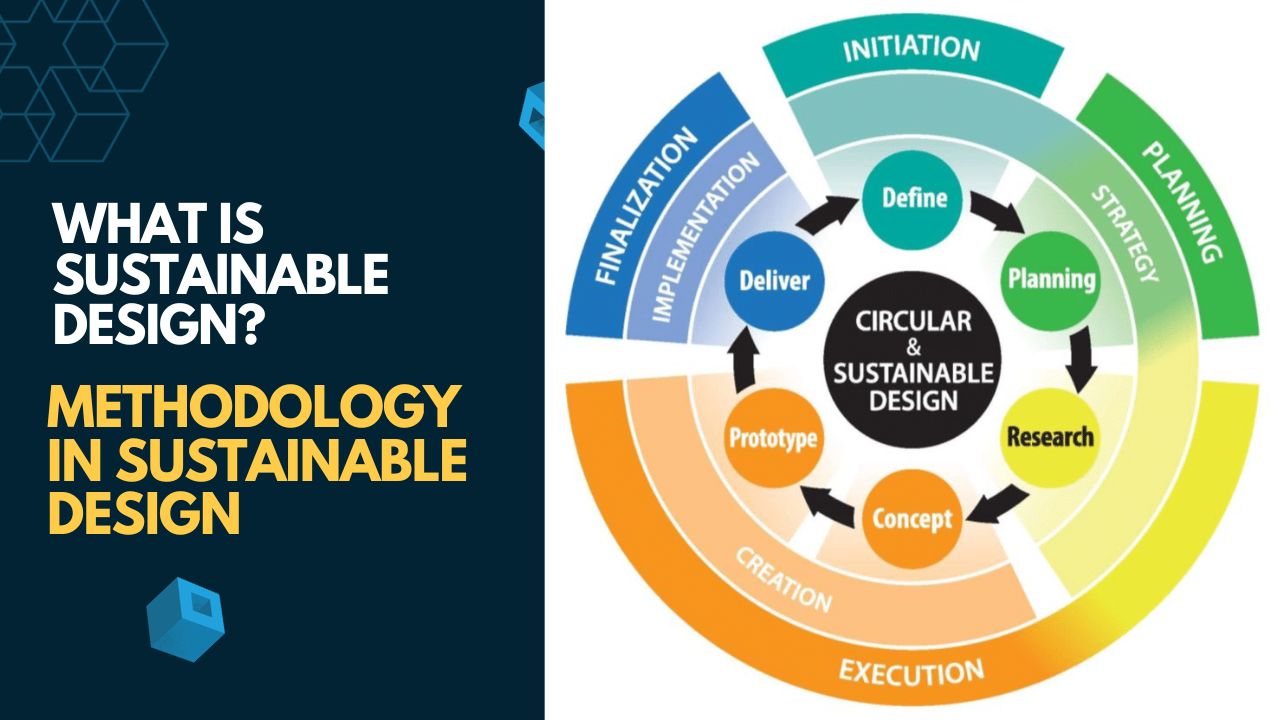
Methodology In Sustainable Design & Construction
Key principles and methodologies in sustainable design and construction include:
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA):
LCA involves evaluating the environmental impacts of a building or infrastructure project from raw material extraction, through construction and use, to end-of-life considerations. This holistic approach helps identify areas where improvements can be made to reduce overall environmental impact.
Energy Efficiency:
Sustainable buildings aim to minimize energy consumption through design features such as proper insulation, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and the use of renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
Material Selection:
Sustainable construction emphasizes the use of eco-friendly and recycled materials. This includes choosing materials with low embodied energy, minimizing waste, and selecting products that have been responsibly sourced and manufactured.
Water Efficiency:
Sustainable buildings incorporate water-efficient technologies such as low-flow plumbing fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and drought-resistant landscaping to reduce water consumption.
Site Selection and Design:
Thoughtful site selection and design can minimize the environmental impact of a project. This includes preserving natural habitats, minimizing disturbance to ecosystems, and optimizing the use of existing infrastructure.
Waste Reduction:
Sustainable construction seeks to minimize waste through efficient construction practices, recycling materials, and implementing waste management strategies. This can include salvaging materials from existing structures and utilizing construction waste for other purposes.
Renewable Energy:
Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, helps reduce reliance on non-renewable resources and lowers a building’s carbon footprint.
Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ):
Sustainable buildings prioritize the health and well-being of occupants by considering factors like air quality, natural light, and thermal comfort. This can contribute to increased productivity and a better overall living or working environment.
Adaptability and Resilience:
Designing structures that can adapt to changing needs and withstand environmental challenges, such as extreme weather events, contributes to the long-term sustainability of the built environment.
Certification Systems:
Various certification systems, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), and others, provide standards and benchmarks for sustainable design and construction. Compliance with these standards helps ensure that a project meets recognized sustainability criteria.
Sustainable design and construction methodologies continue to evolve as new technologies and practices emerge, reflecting a growing awareness of the need for environmentally responsible and socially conscious approaches in the construction industry.